American Cheese vs. Cheddar: Differences, Benefits, and Nutrition


The average American adult eats almost 42 pounds of cheese yearly.1 Cheddar is America’s favorite cheese, and American cheese is in the top five most popular cheeses in the United States.2 Americans love to eat cheese.
You may wonder about the difference between these two popular cheeses and whether a specific type of cheese is superior.
American cheese, a processed cheese, is best known for its mild, creamy flavor and superior melting.
Cheddar cheese is a hard, natural cheese with a sharper taste and crumbly texture.
This article will highlight the main differences, nutrition comparisons, how each cheese is made, the best uses for each cheese, and any health issues to be aware of with each cheese.

Discover how your body responds to what you eat, and make small changes to hit your health goals
View PlansWhat Is American Cheese?
American cheese is a processed dairy product made of at least two cheeses melted with cream or milk and other ingredients.
This cheese melts easily, has a long shelf life (six months in the refrigerator and within a week if the package is opened), has a consistently mild and creamy flavor, and a medium-yellow color.
What Is Cheddar Cheese?
Cheddar cheese is a natural, hard cheese made traditionally (heat, milk, microorganisms, salt, and enzymes). Cheddar cheese does not melt as well as American. It can range from a mild flavor to a very sharp or pungent taste.
Cheddar can also be white, pale yellow, or bright orange. It can be stored in the refrigerator for six months before opening and three to four weeks after opening.
What Is the Difference Between American Cheese and Cheddar Cheese?
Cheese-making has existed for over 9,000 years. Originally, cheese was made to preserve milk and make the nutrients available for later consumption before refrigeration.3
Natural cheese is produced by fermenting, heating, and removing the water from milk, leaving concentrated milk protein, fats, and nutrients.
The cheese is fermented by adding microorganisms, salt, and enzymes. The curds (the solid portion of the milk) are drained from the whey (the liquid portion of the milk). Some cheeses are ripened or aged in as little as two months up to five years. Cheddar is aged between two and twelve months.3
Different types of milk, the type and amount of microorganisms (starter culture), and the length of ripening affect the natural cheese flavor.3
Cheddar takes on a sharp or pungent flavor with more time. It is a hard cheese and does not spread well due to its low moisture content, especially with a more aged cheddar. As cheddar ages, it has less moisture and becomes more crumbly.3
Mild cheddar is aged less and melts better. Extra sharp cheddar is better for a cheese platter, on a cold sandwich, or paired with fruit. You can melt shredded cheddar with milk, butter, and flour (a roux) on the stove for a creamy cheese sauce.
Cheddar ranges from white and pale yellow to dark orange. The dark orange color comes from annatto, a fruit-based coloring.4
American cheese is a processed cheese product, and per the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), its official name is pasteurized processed American cheese.5
It was developed in 1911 in Switzerland by heating shredded Swiss cheese with sodium citrate, an emulsifying agent, to make a shelf-stable cheese product.6
Kraft cheese was patented in 1916 with a slightly different process of heating and whisking melted cheddar cheese to make American cheese in blocks. Eventually, a method for slicing American cheese was developed.6
The processed American cheese today is made from a blend of at least two cheeses (commonly cheddar or colby cheese), making up at least 51% per the FDA.5
Other ingredients include emulsifiers and acidifying agents, water, salt, cream or milk products, artificial coloring, and spices or flavorings. The emulsifying agents are what allow American cheese to melt effortlessly.5
Due to the mixture of cheeses and the addition of cow’s milk or cream, American cheese has a mild, creamy flavor, medium-yellow color, and a smooth texture that easily melts.
American cheese is used on sandwiches like grilled cheese sandwiches, cheeseburgers, or dishes that use melted cheese.
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) regulates American cheese's acceptable flavor, texture, meltability, and food coloring.7
The FDA and USDA oversee the safety of all cheeses (natural and processed). They state that cheese can be made safely in two ways - using pasteurized milk or raw or unpasteurized milk aged for at least 60 days at a temperature of 35 degrees Fahrenheit.3
Which One Is Better: American Cheese or Cheddar Cheese?
Both American and cheddar cheese are higher in fat content and calories. Cheddar cheese is slightly higher in fat and saturated fat but lower in sodium.
Neither cheese is something to overeat. When you compare cheese to nutrient-rich fruits and vegetables, determining the health benefits of cheese is easier to understand.
Generally, eating large amounts of fruits and vegetables has little consequence. These fruits and vegetables provide large amounts of fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals that benefit health.
American and cheddar cheeses contain moderate (not high) calcium, vitamin A, phosphorus, and selenium, respectively. American cheese also contains higher amounts of vitamin D.
Cheese is not considered a powerhouse for vitamins and minerals. Cheese does not contain fiber.
Cheese is primarily a fat and protein source with few vitamins and minerals. It is meant to be eaten with a diet prioritizing lean protein like chicken and fish, fruits, vegetables, beans, whole grains, and heart-healthy fats like olive oil and nuts.
Cheddar is lower in sodium and has more protein than American cheese. For individuals monitoring sodium levels, cheddar is a better choice.
Excess sodium can increase blood pressure in some people. High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Lower sodium diets can reduce your risk of heart disease and kidney disease.8
For the average person, either cheese is acceptable. Monitoring your total fat, saturated fat, and sodium intake from other foods ensures you can enjoy cheddar or American cheese in moderation.
Cheddar cheese is a more suitable option if you are limiting processed foods.
American Cheese vs. Cheddar: Nutritional Facts
For the comparison tables, a single slice (21 g) of each cheese is used for comparison.9, 10
When comparing the two cheeses, calories are similar. Next, fat amount and type are important to consider.
Diets high in saturated fat are associated with heart disease. Large randomized controlled trials indicate that reduced dietary saturated fat (or less than 10% of total calories) reduces the risk of heart events by 21%.11
Ten percent of total calories for a 2,000-calorie diet equals 22.2 g of saturated fat or less daily.
Cheddar cheese contains 7.1 g of fat and 4g from saturated fat. American cheese is slightly lower in fat (5.9g) and saturated fat (3.4g).
Sodium is another factor to consider when making choices. Limiting sodium to 2,300 mg daily is recommended by the American Heart Association.8
Consuming too much sodium can increase blood pressure in salt-sensitive individuals. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease.8
Foods high in sodium tend to lack vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Lower sodium diets can reduce your risk of heart disease and kidney disease.8
American cheese contains 317mg of sodium, while cheddar cheese is lower at 137mg as it is less processed.
Both cheeses are low in carbohydrates and fiber. Most of the calories come from fat and protein. When fat and protein are combined with high-fiber carbohydrates like fruits, vegetables, and beans, you feel full longer and snack less.
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of cheddar cheese is 0, classifying it as a food with a low glycemic index.12
American cheese does not have a calculated glycemic index, but it contains similar nutrients but with marginally more carbohydrates. It is still considered a low glycemic index food.
The minimal carbohydrates paired with fat and protein content help stabilize blood sugar levels and keep you full longer.
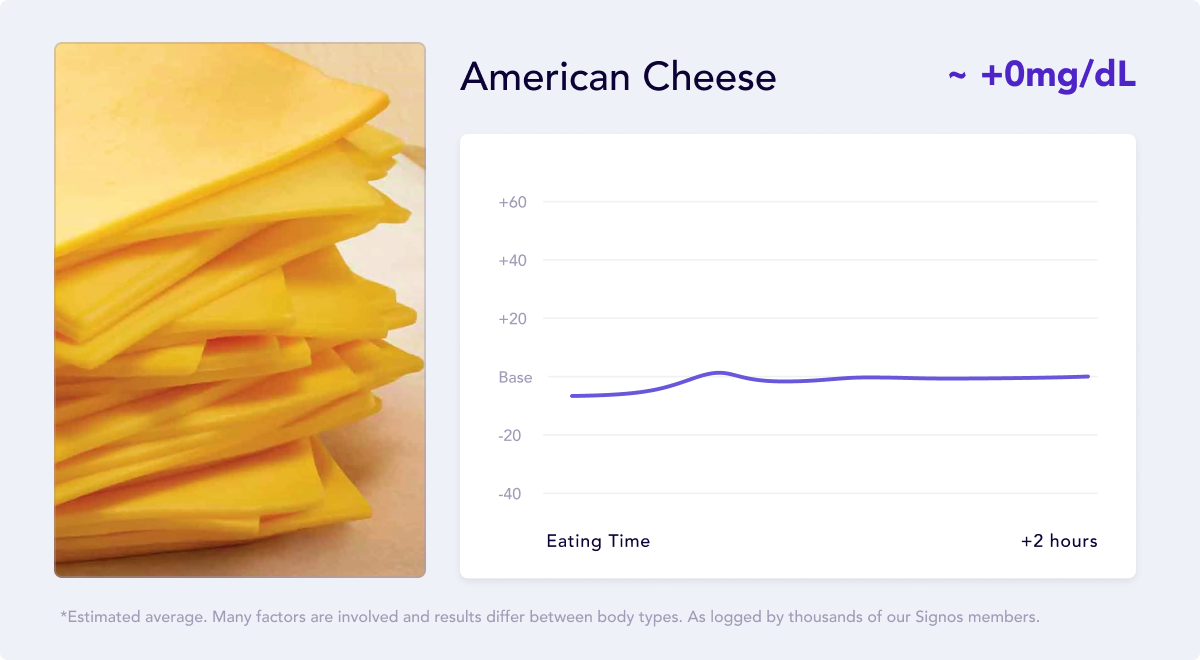
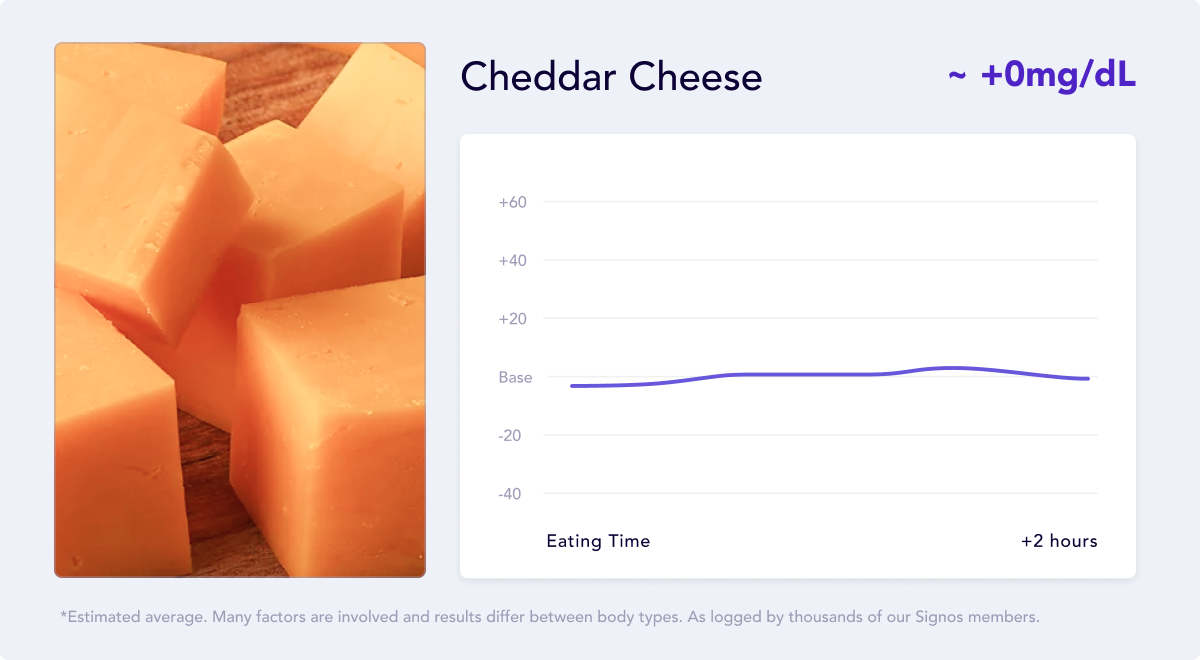
Vitamins & Minerals
American and cheddar cheese are similar in vitamins and minerals, except for calcium, vitamin D, sodium, and selenium.
American cheese contains 8% DV of vitamin D compared to 1% DV for cheddar cheese.
Calcium is slightly higher in American cheese at 15% DV compared to 11% cheddar cheese.
Sodium is lower for cheddar cheese at 137mg (6% DV) than American cheese at 317mg (14% DV). Individuals should limit sodium intake to 2,300mg daily.
Selenium is slightly higher in cheddar cheese (11% DV) than in American cheese (7% DV).

Discover how your body responds to what you eat, and make small changes to hit your health goals
View PlansReferences
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Cheese Is Best for Us?
If you limit sodium intake and want to reduce processed food, cheddar cheese is better since it is lower in sodium and less processed.
Other than sodium, both cheeses are similar in nutritional value. American Cheese has higher vitamin D. Cheese does not usually raise blood sugar levels.
Is American Cheese 100% Real Cheese?
American cheese is made with 100% real cheese, which makes up 51% of the processed food product. The other portions are emulsifying and acidifying agents, water, salt, cream or milk products, artificial coloring, and spices or flavorings.
Why Does American Cheese Melt So Well?
American cheese has emulsifying agents that help it melt well and stay creamy.
Hard cheeses often need to be shredded and added to a milk, butter, and flour mixture to melt well. They often cannot maintain the creamy texture for long.
What Cheese Is 100% Cheese?
Cheddar cheese is 100% cheese, along with other non-processed cheeses like Swiss, mozzarella, Colby, Monterrey Jack, and Parmesan cheese.

